Proximity Detection During Epidemics: Direct UWB TOA Versus Machine Learning Based RSSI.
Zhuoran Su, Kaveh Pahlavan, Emmanuel Agu, Haowen Wei
International Journal of Wireless Information Networks, 29(4), 2022.
Duration: May 2021 – August 2022
Role: Software Engineer
Advisor: Dr. Kaveh Pahlavan & Dr. Emmanuel Agu
Overview
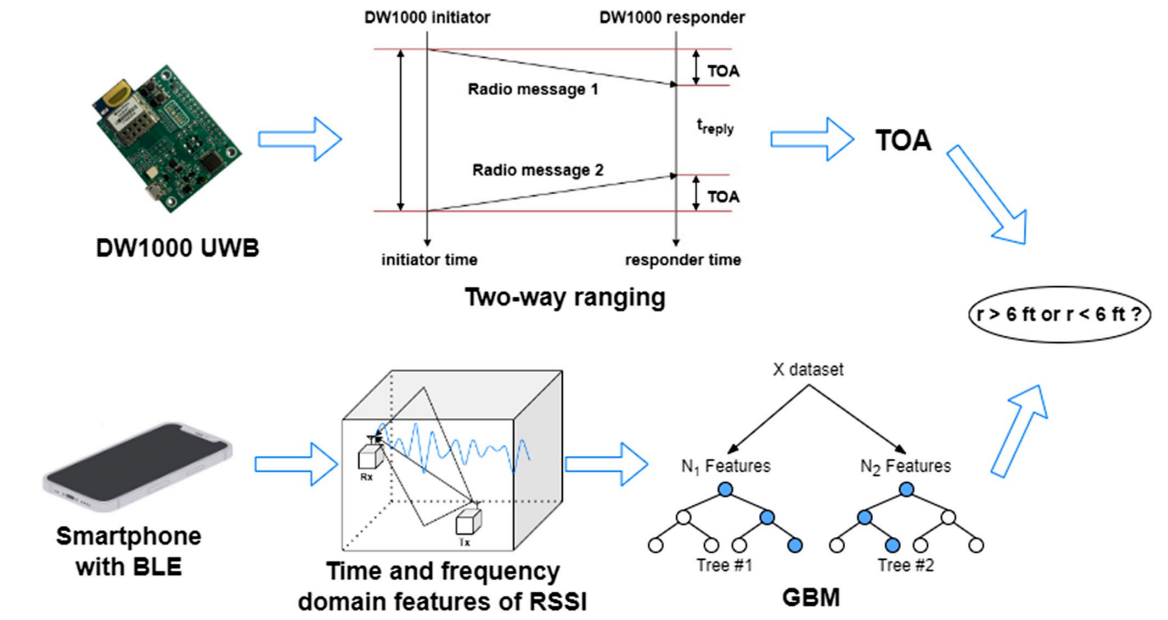
This study compares the proximity detection performance of Ultra-Wideband (UWB) Time of Arrival (TOA) and Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) Received Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI) enhanced by machine learning. By evaluating their accuracy and computational complexity in various environments, including Line-of-Sight (LOS) and Obstructed-Line-of-Sight (OLOS) scenarios, the research aims to shed light on the reliability of UWB and BLE for real-time proximity detection during epidemics.
My Contributions
- Data Collection Pipeline: Designed and developed the UWB data collection pipeline, ensuring accurate data capture for a fair comparison with BLE RSSI in identical environments.
- Software Engineering: Implemented and optimized the experimental setup, enabling seamless data processing and real-time analysis.
Contributions of the Study
- Empirical Comparison: Provides a comprehensive comparison between UWB TOA and BLE RSSI enhanced by machine learning for proximity detection.
- Real-World Scenarios: Assessed the performance of UWB and BLE in various settings, including both LOS and OLOS conditions.
- Key Findings: Highlighted the advantages of UWB in terms of higher accuracy and lower computational complexity, offering valuable insights for its application in real-time proximity detection during epidemics.